Understanding Forefoot Ulcers
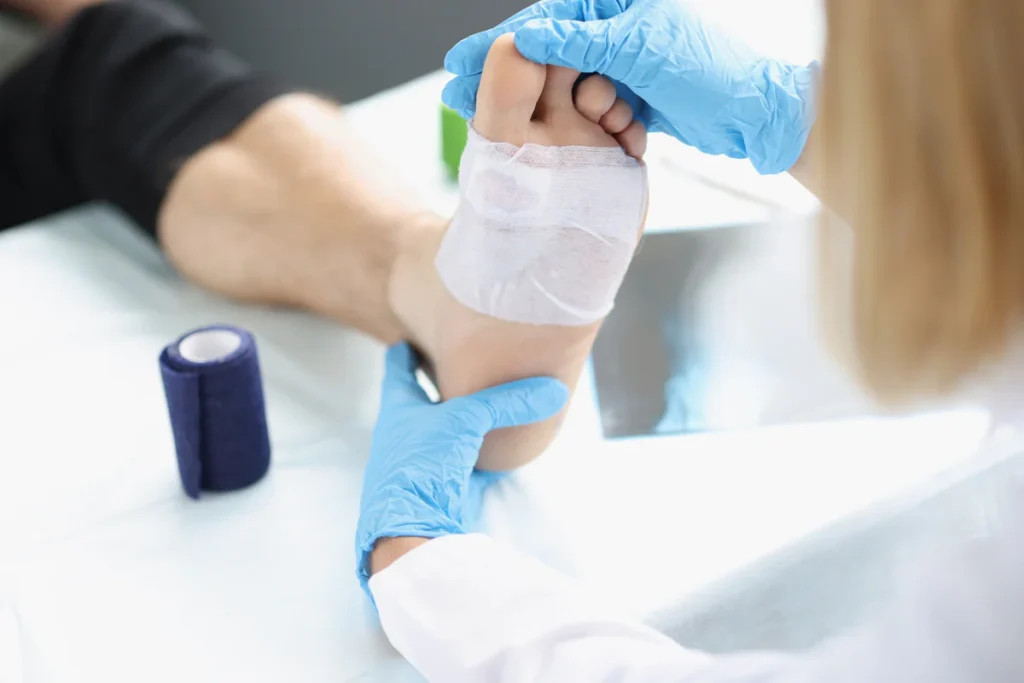
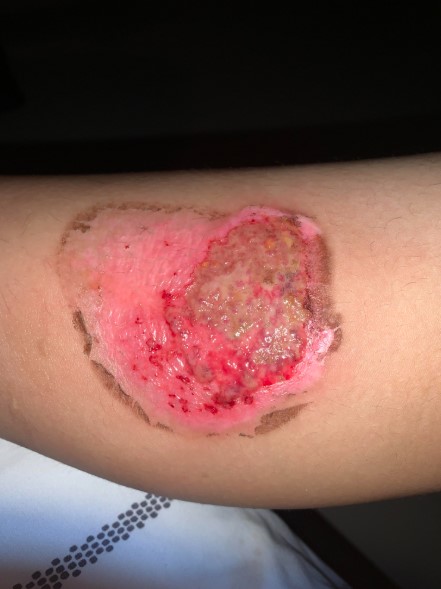
Forefoot ulcers are painful wounds that typically develop on the ball of the foot or the toes, and they often affect individuals with diabetes or poor circulation. These ulcers form when constant pressure, friction, or underlying medical conditions cause skin breakdown, exposing deeper tissues to infection. Common contributors include neuropathy, where nerve damage reduces sensation in the feet, and peripheral arterial disease, which limits blood flow and delays healing. Ill-fitting shoes or repetitive stress can worsen the condition, leading to open sores that resist healing. Many patients ignore the early warning signs, such as redness, swelling, or minor cuts, until the ulcer progresses. Left untreated, these ulcers can spread infection to surrounding tissues and bones, making recovery more difficult. Recognizing the earliest symptoms and understanding how forefoot ulcers develop is the first step toward proper care and prevention.
The Role of Orthopedic Care in Managing Forefoot Ulcers
Orthopedic specialists play a vital role in diagnosing and managing forefoot ulcers by examining the mechanics of the foot and identifying pressure points that contribute to wound formation. Unlike general wound care providers, orthopedic experts focus on both healing the existing ulcer and preventing recurrence by correcting structural issues. They assess walking patterns, bone alignment, and skin integrity to create a tailored treatment plan. Early intervention is essential because orthopedic care goes beyond surface healing—it addresses the root cause of the problem. For instance, correcting gait abnormalities or providing custom support devices can drastically reduce stress on vulnerable areas. Orthopedic professionals also collaborate with podiatrists and vascular specialists when necessary, ensuring a holistic approach to patient care. Their involvement is especially crucial for high-risk individuals, such as those living with diabetes, since they often face a higher likelihood of chronic wounds. By blending wound care with orthopedic expertise, patients benefit from more effective and lasting results.
Common Orthopedic Treatment Options for Forefoot Ulcers
Orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers typically begins with offloading techniques designed to remove pressure from the affected area. Specialized footwear, orthotic inserts, and total contact casts are among the most common methods used to protect the ulcer while allowing it to heal. If conservative options fail to produce results, surgical procedures may be recommended to correct deformities or relieve persistent pressure. Orthopedic surgeons may also employ advanced wound dressings, skin grafts, or biologic materials to speed recovery and reduce infection risk. Another essential aspect of treatment is physical therapy, which helps patients maintain mobility while supporting proper healing. Therapy may include exercises to strengthen surrounding muscles, improve balance, and prevent falls that could worsen the condition. Each treatment plan is tailored to the individual, ensuring that their unique medical history, activity level, and risk factors are taken into account. The ultimate goal of orthopedic interventions is not just healing but also preventing future ulcer formation.
The Importance of Proper Footwear and Orthotics
Proper footwear plays a central role in preventing and managing forefoot ulcers. Orthopedic shoes are designed to evenly distribute weight across the foot, reducing localized pressure on vulnerable areas. Custom orthotics, such as insoles and inserts, provide added support and cushioning that can make a significant difference for patients with neuropathy or circulation problems. By reducing friction and correcting misalignments, orthotics lower the risk of repeated ulcer development. Orthopedic specialists often recommend footwear made with breathable materials and adequate room for the toes, ensuring comfort and protection. For individuals with diabetes, wearing the correct shoes can mean the difference between a stable lifestyle and chronic foot complications. These devices are not a one-size-fits-all solution but are carefully adjusted based on a patient’s needs. Investing in proper footwear and custom orthotics is one of the most effective preventive strategies for long-term ulcer management.
Preventive Measures in Orthopedic Care
Preventing forefoot ulcers requires consistent attention to foot health, and orthopedic care emphasizes proactive measures. Daily routines such as checking for cuts, blisters, or changes in skin color are strongly encouraged, especially for individuals with diabetes. Orthopedic specialists often recommend weight management, as excess pressure from added body weight can increase the likelihood of ulcers forming. Regular check-ups allow physicians to monitor changes in foot structure and function, catching potential problems before they worsen. Proper hygiene, moisturizing the skin to prevent cracks, and trimming toenails carefully all play essential roles in overall prevention. Orthopedic care also includes teaching patients how to recognize early warning signs, empowering them to seek treatment quickly. Lifestyle adjustments, including balanced nutrition and blood sugar control, further support prevention efforts. By combining medical oversight with daily self-care, patients significantly reduce their risk of recurring ulcers.
Long-Term Impact of Untreated Forefoot Ulcers
Ignoring forefoot ulcers can have severe consequences that extend beyond localized pain. Persistent wounds increase the risk of infections, which can spread to surrounding tissues and even into the bone, leading to osteomyelitis. This not only complicates treatment but also poses serious threats to mobility and overall health. Without timely orthopedic intervention, patients may face a greater likelihood of partial or complete amputation. The loss of mobility that results from untreated ulcers can lead to further complications such as muscle weakness, weight gain, and reduced independence. On an emotional level, chronic pain and limited activity often contribute to feelings of frustration, stress, and diminished quality of life. Orthopedic care helps mitigate these risks by addressing both the physical and emotional challenges associated with ulcers. Taking action early prevents these long-term complications and allows patients to maintain a healthier, more active lifestyle.
The Patient’s Role in Orthopedic Healing
While orthopedic specialists provide expert care, the patient’s commitment to treatment plays a critical role in recovery. Following medical advice, adhering to prescribed treatments, and attending scheduled appointments are essential for healing success. Patients with diabetes must also prioritize blood sugar control, as uncontrolled glucose levels can delay wound healing and increase the likelihood of recurrence. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in nutrients supports tissue repair, while regular, safe physical activity strengthens circulation and mobility. Patients should also avoid smoking, as it restricts blood flow and significantly slows healing. Building a strong partnership with the orthopedic team allows for continuous monitoring and adjustments in care. By taking responsibility for their health and working closely with their specialists, patients can achieve better outcomes and long-term stability.
FAQ Section
What is the best orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers?
The best treatment depends on the severity and cause of the ulcer. Orthopedic specialists often start with offloading techniques, such as custom shoes or inserts, and may progress to surgical options if necessary.
How long does it take for a forefoot ulcer to heal with orthopedic care?
Healing time varies depending on the patient’s overall health, circulation, and treatment compliance. Some ulcers may heal within weeks, while others require several months of consistent care.
Can orthopedic shoes really prevent ulcers from coming back?
Yes, orthopedic shoes and custom orthotics help distribute pressure evenly, reduce friction, and protect the foot, making them an effective strategy for preventing recurrence.
When should I see an orthopedic specialist for a foot ulcer?
You should seek care immediately if you notice any open wounds, persistent redness, or signs of infection on your forefoot, especially if you have diabetes or poor circulation.
Are surgeries always necessary for treating forefoot ulcers?
No, surgery is usually considered only when conservative treatments fail. Most patients respond well to offloading, wound care, and proper footwear before surgical options are explored.