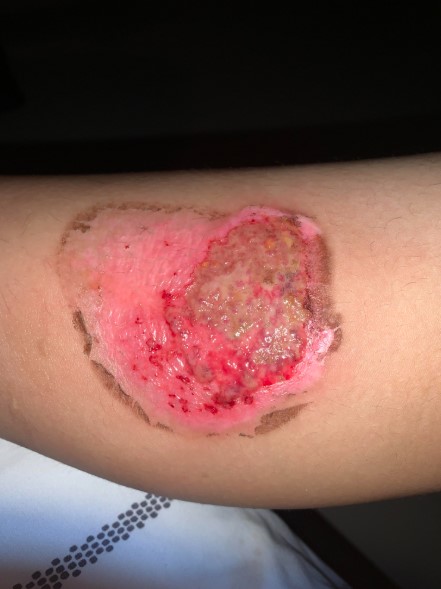
Non-healing wounds are a persistent medical challenge that can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. Unlike ordinary wounds that heal within weeks, non-healing wounds linger, often causing chronic pain, infections, and mobility issues. When wounds fail to heal, orthopedic complications are often a contributing factor, particularly when bones, joints, or surrounding tissues are affected. Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds is essential because it addresses both the surface wound and underlying musculoskeletal conditions that impede healing. Factors such as diabetes, poor circulation, infection, trauma, and structural issues can all slow recovery. Early recognition and professional evaluation can prevent severe complications, including tissue necrosis or systemic infection. By seeking timely orthopedic care, patients can receive tailored interventions designed to accelerate healing and reduce long-term risks.
Signs That a Wound Requires Orthopedic Attention
Identifying when a wound requires orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds is crucial. Persistent redness, swelling, and pain are often the first signs that a wound is not healing properly. Wounds that remain open for several weeks despite basic care, or those producing unusual discharge or odor, indicate a need for specialist evaluation. Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds focuses on detecting deeper structural issues that general wound care may overlook. Bone or joint involvement, compromised blood flow, or repeated pressure injuries often require intervention from orthopedic specialists. Pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, and post-surgical wounds are particularly at risk. Early orthopedic assessment ensures that patients receive targeted therapies to prevent deterioration and promote recovery.
Role of Orthopedic Specialists in Wound Management
Orthopedic specialists play a key role in the management of non-healing wounds by addressing underlying musculoskeletal complications. Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds begins with a thorough assessment, including physical examinations, imaging, and laboratory tests. These evaluations help identify infections, bone involvement, or circulatory issues that may impede healing. Orthopedic specialists often collaborate with podiatrists, vascular surgeons, and infectious disease experts to create a comprehensive treatment plan. This multidisciplinary approach ensures both the wound and its underlying causes are addressed. Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds includes interventions that improve blood flow, relieve pressure, and stimulate tissue repair. By addressing the root causes of chronic wounds, orthopedic care significantly increases the chances of successful and lasting healing.
Advanced Orthopedic Treatment Options
For persistent wounds that fail to respond to conventional care, advanced orthopedic interventions are often necessary. Surgical procedures such as debridement, skin grafting, or reconstructive surgery are frequently part of orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds. These procedures remove infected or necrotic tissue and promote optimal conditions for healing. Bone stimulation techniques, such as electrical stimulation or low-intensity ultrasound therapy, may also be employed to accelerate tissue regeneration. Orthopedic devices like braces, casts, or specialized supports can reduce pressure on affected areas and improve circulation. Emerging regenerative therapies, including stem cell therapy and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatment, show promise in supporting tissue repair and accelerating recovery. Advanced orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds is highly personalized, with interventions designed to meet the unique needs of each patient.
Non-Surgical Orthopedic Approaches
Not all wounds require surgical intervention. Non-surgical orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds often provides effective alternatives. Specialized dressings, including hydrocolloid or foam dressings, maintain proper moisture balance and protect wounds from contamination. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) uses controlled suction to promote tissue regeneration and reduce fluid buildup. Physical therapy can enhance blood circulation, improve mobility, and reduce stiffness around the affected area, supporting wound healing. Pain management strategies help patients maintain comfort and quality of life throughout the recovery process. Nutritional guidance, including adequate protein and essential vitamins, supports tissue repair and immune function. Combining non-surgical orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds with lifestyle adjustments, such as offloading pressure from high-risk areas, optimizes healing without invasive procedures.
Preventing Recurrence and Promoting Long-Term Healing
Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds also focuses on preventing recurrence and ensuring long-term wound management. High-risk patients, such as those with diabetes or vascular disorders, require regular monitoring to detect new wounds early. Custom orthotics or footwear can prevent pressure ulcers and redistribute weight to minimize tissue stress. Lifestyle modifications, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper wound hygiene, support sustained tissue health. Ongoing follow-ups with orthopedic specialists help identify potential complications before they escalate. Educating patients about proper wound care at home empowers them to take control of their recovery. By combining proactive monitoring, professional care, and lifestyle adjustments, orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds can significantly reduce the likelihood of recurrence and improve overall patient outcomes.
Patient Experiences During Orthopedic Treatment
Patients undergoing orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds often experience a combination of clinical care and home-based strategies. Initial appointments typically involve detailed assessments, including imaging and laboratory tests, to determine the underlying cause of delayed healing. Treatment plans may include surgical or non-surgical interventions, as well as lifestyle and nutrition recommendations. Daily home care is crucial, including dressing changes, hygiene practices, and monitoring for signs of infection. Emotional support is an important aspect of care, as chronic wounds can cause frustration, stress, and anxiety. Counseling or support groups may be recommended to help patients manage these challenges. Open communication with orthopedic specialists ensures that patients understand their treatment, set realistic expectations, and achieve optimal results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What defines a non-healing wound that requires orthopedic treatment?
Non-healing wounds are wounds that fail to improve significantly within four to six weeks. Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds is recommended when there is suspected bone involvement, infection, or chronic structural complications. - How long does it take for an orthopedic-treated wound to heal?
Healing time varies depending on the severity of the wound, the patient’s overall health, and the treatment method. Advanced orthopedic interventions often accelerate healing, but chronic wounds may take several weeks to months to close fully. - Are there risks associated with surgical orthopedic treatments?
Surgical treatments carry potential risks, such as infection, bleeding, or delayed healing. Orthopedic specialists carefully plan procedures to minimize risks and optimize recovery outcomes. - Can non-surgical methods alone be effective for certain patients?
Yes, non-surgical orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds, including negative pressure therapy, specialized dressings, physical therapy, and nutritional support, can be effective when combined with preventive measures. - How can patients prevent future non-healing wounds?
Preventive strategies include maintaining proper wound hygiene, using custom orthotics or footwear, managing chronic conditions like diabetes, and following lifestyle adjustments recommended by orthopedic specialists.